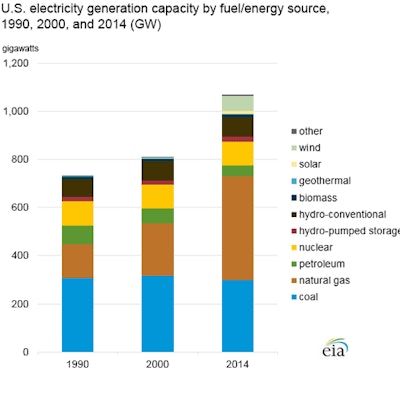
A recent report from the U.S. Energy Information Administration offers a look at the changing face of fuel sources for the generation of U.S. electricity since 1990. A more complete perspective can be seen by viewing the chart in the galley. Recapping EIA's findings:
- In 1990 coal-fired power plants accounted for about 42 percent of U.S. electricity generation capacity, but produced more than half of the total electricity supply. By the end of 2014, coal's share decreased to 28 percent and accounted for 39 percent of electricity generation.
- Over the same period, the share of natural gas-fired electric generation capacity more than doubled from 19 percent in 1990 to 40 percent in 2014, as did the share of actual generation from natural gas, rising from 12 percent to 28 percent.
- Both nuclear and hydro-power electric generation capacity grew slightly.
- Nuclear's share of the total amount of U.S. electricity generated held steady at about 20 percent.
- Electricity generation from wind experienced significant gains in its share of electric generation capacity, growing from 0.2 percent in 1990 to about six percent in 2014.
According to EIA, the major factors contributing to changes in the U.S. electricity generation mix in recent years are:
- Declining natural gas prices.
- Slowing growth in electricity demand.
- Implementing federal air pollution emission regulations.
- Meeting state requirements to use more renewable sources.
- Using federal and state financial incentives for renewable resources.
Looking forward, despite the scheduled closure of more than 2 GW of nuclear generating capacity by 2019, almost 6 GW of nuclear generating capacity is scheduled to be added between 2016 and 2020. In 2013, four nuclear power reactors were taken out of service, and in 2014 the Vermont Yankee nuclear power plant was also retired.
For a look at the complete report , go to https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/electricity/electricity-in-the-us.php






















